A. CLASSIFICATION:
Division – Psilophyta
Class – Psilotopsida
Order – Psilotales
Family – Psilotaceae
Genus – Psilotum
Division – Psilophyta
Class – Psilotopsida
Order – Psilotales
Family – Psilotaceae
Genus – Psilotum
The
genus Psilotum is widely distributed
in the tropical and sub-tropical regions of both Northern and Southern
hemisphere, (e.g. – P. nudum and P. flaccidium). The plant is xerophytic
in nature and grows in various habitats from very dry to moist places. They are
also found to grow on tree ferns and palms.
P. nudum is found to grow
in India, and hence it is the only Indian species.
B. STRUCTURE OF THE
SPOROPHYTE:
1. External structure:- The sporophyte, i.e., the plant body is well
differentiated into – a slender rootless rhizome and an aerial shoot.
Rhizome – The rhizome contains a mycorrhizal fungus
and is covered with hair like rhizoids. The branching of the rhizome is
dichotomus. Some of the dichotomy may become erect and develop into green
aerial leafy shoot.
Aerial shoot – Aerial shoots are either pendent (in case
of epiphytic condition), or erect (in case of terrestrial condition). The
branching of aerial shoot is strictly dichotomous.
Leaves
– The aerial branches bear on the upper part, small, scale like appendages, i.e.,
leaves, arranged in 2-3 rows.
2. Internal structure:- (a) T.S of Aerial
Shoot: Internal structure of aerial shoot shows the
following tissue systems –
Epidermis – Epidermis of aerial shoot is one-celled in
thickness with heavily cutinized outer wall. The epidermis is interrupted by
the presence of stomata.
Cortex – Cortex is broad and differentiated into
3-regions – (a) hypodermal outer cortex
composed of chlorenchymatous cells, 2-5 layers thick, (b) middle cortex composed of thick walled sclerenchymatous cells, 4-5
layers thick, and (c) an inner cortex
composed of thin walled parenchymatous cells, containing abundant starch
grains. The innermost layer of the cortex is the single layered endodermis with
casparian strips.
In rhizome, cortex is composed of only thin walled
parenchymatous cells containing mycorrhizal fungus.
Stele – The stele of aerial shoot is actinostelic protostele, with 5-6 xylem
rays. The xylem rays are exarch. Phloem lies in the outer portion, covering the
xylem, beneath the endodermis. Phloem cells are made up of thin-walled cell
elements and sieve tubes.
The stele of rhizome is haplostelic or actinostelic
type of protostele. Central xylem
core is completely surrounded by the phloem.
(b)
T.S of Leaf:
The T.S of leaf shows a single layered epidermis. Stomata are absent in the
epidermal layer. Beneath the epidermis is an undifferentiated chlorenchymatous
mesophyll cells. There is no vascular tissue in the leaf of Psilotum.
C. REPRODUCTION:
The sporophyte of Psilotum
reproduces both by vegetative means and by production of spores –
1. Vegetative Reproduction:- Vegetative reproduction in Psilotum takes place by the formation of
gemmae. The gemmae are developed in
large numbers on the rhizomes. The gemma may germinate into new plant when it
is still attached to the parent plant or when they fall on the suitable
substratum after detachment.
2. Spore Formation:- In Psilotum,
the spores are formed in a specialized spore bearing structure, known as sporangia. The sporangia are borne in
triads on the vertical side of the appendage, i.e., leaf, at the point of
dichotomy and are slightly raised by short stalk. The sporangia are fused with
one another, and such group of sporangia is known as synangium.
Each
mature synangium is 2-3 mm wide, 3-lobbed and each lobe contains a spore sac,
in which numerous spores are present. Psilotum
is homosporous, i.e., it produces only one type of spores.
D. STRUCTURE OF THE
GAMETOPHYTE:
Spore is the first cell of the gametophyte. Each spore is
bilaterally symmetrical with outer delicate and thin reticulate wall. The spore
germinates after about 4 months of liberation, and develops into a gametophytic
plant body.
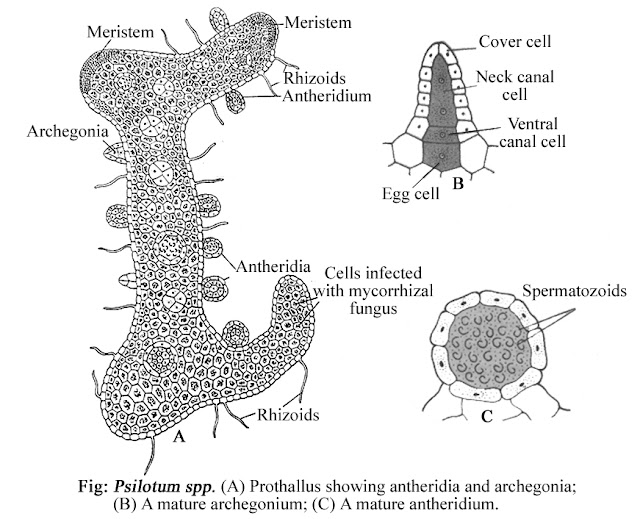
The gametophytic plant body is very small (about 18 mm
long), brown in colour, sub-terranean and sporophytic in nature. The mature
gametophyte is dichotomously or irregularly branched and is covered with dense,
brown, hair-like rhizoids and is filled with mycorrhizal fungus.
Gametophytes are monoecious, i.e.,
they are homothallic. Both the sex organs, i.e., antheridia and archegonia
are borne on the same gametophytic plant body.
1. Antheridia:- Antheridia begin to develop on the
gametophyte earlier than the archegonia. Each antheridium is a projected
spherical body, covered by a single layer of jacket cells. Within the jacket layer, lies numerous sperm mother cells, which metamorphose into numerous
spiral, multiflagellate sperms, i.e.,
antherozoids.
2. Archegonia:- The archegonia are shunken with short
projecting neck, which breaks away at
maturity. The neck consists of 4-5 cells long, and consists of 2 neck canal cells. The venter consists of one ventral canal cell and an egg cell.
3.
Fertilization:- At maturity, the neck of the archegonium
breaks, followed by the disintegration of the neck canal cells, which leaves a
passage for the entry of sperms. The sperms after liberation from the
antheridium, makes its way through the archegonial neck and finally reaches the
egg. On reaching the egg, one sperm fuses with the egg to complete the fertilization.
As
a result of fertilization, a diploid zygote (2n) is formed. With the formation
of zygote, diploid sporophytic generation begins.
****************







seleginella notes
ReplyDeleteVery useful for me
ReplyDeleteWhp is the authore of this?
ReplyDeleteThank you so much..
ReplyDeleteIt's very useful for me
The presentation of this chapter is very simple, which makes easily understandable.
ReplyDeleteGive morphology of psilotum
ReplyDeleteThankyou so much....its really very useful
ReplyDeleteVery Useful
ReplyDeleteIt's good am happy to your job be contionus blessed
ReplyDelete
ReplyDeleteThis blog is very effective and valuable. I am very glad to read your blog.
high quality shilajit
both Meaning In Hindi
ReplyDelete